Cardiovascular Diseases
Supraventricular Ectopic Activity
The Holter (dynamic electrocardiography) is a widely used non-invasive method for this assessment. Here we will look at criteria for the evaluation of atrial extrasystoles.
The evaluation of arrhythmias and clinical-electrocardiographic correlation assumes a fundamentally important aspect in cardiological practice. The Holter (dynamic electrocardiogram) is a widely used non-invasive method in this evaluation. Here we will see criteria for the evaluation of atrial ectopic beats.
The observation of atrial ectopic beats is relatively frequent in clinical practice observed after the 4th decade, mainly.
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHIC CRITERIA FOR IDENTIFICATION TO HOLTER
Premature P waves (P’) with P’R interval greater than 120 milliseconds.
P’ morphology slightly different from the sinus P wave (rarely resembling).
Coupling Period (P-P’) constant.
Incomplete post-ectopic pause.
The majority of atrial ectopic beats normally conduct through the conduction system, configuring “QRS” complexes with morphology similar to the Basal Sinus Rhythm. When atrial ectopic beats encounter the ventricles during the refractory period, they can be blocked (absence of QRS). The diagnosis is often made by the modification of a “T” wave, followed by a pause. On other occasions, the premature impulse of atrial origin reaches the ventricles finding the branches of the His bundle in different states of refractoriness, defining Aberrant Conduction. The morphology of Right Bundle Branch Block is the most frequently observed. Other times, various morphologies of “P” wave suggest the presence of multiple foci of origin (pre-fibrillatory rhythm).
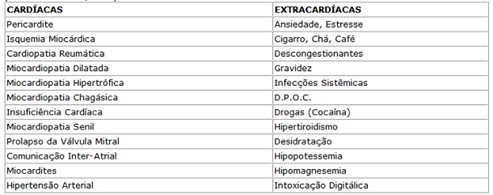
CAUSES OF ATRIAL ECTOPIC BEATS (Dr. Dalmo Moreira, 1995)
The presence of atrial ectopic beats may not entail symptoms. In the clinical correlation made with Holter, the most frequent symptoms are: “palpitations,” “pulse failures,” “flutters,” “stitches,” strong beats in the throat and chest.
We must emphasize that in Holter analysis, observation is performed in 3 channels, with morphological changes of “P,” not adhering to the criteria observed in all ECG cases. The atrial ectopic beat is therefore better defined as supraventricular ectopic beat, and the morphology of “P” (positive, negative, or absent) should be described or analyzed without concerns over specific definitions. Its manifestations can be isolated, paired (bi-tri-quadri), in runs of 2 and 3, and in episodes of non-sustained atrial tachycardia when above 4 consecutive beats. Remember also that the analysis of supraventricular activity (P wave) is not defined with specific “Software.” Its observation is carried out considering criteria of the prematurity of the R-R interval. In other reviews, we will define the criteria for complex activity (Tachyarrhythmias) and criteria for prematurity.
Next, some of the examples mentioned above:
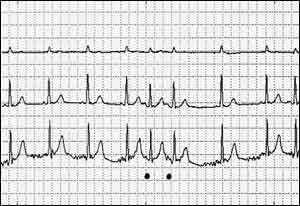
FIGURE 1- ATRIAL ECTOPIC BEAT WITH POSITIVE “P”
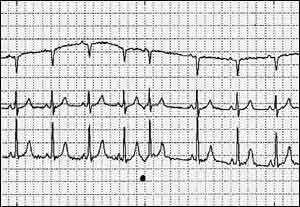
FIGURE 2- ATRIAL ECTOPIC BEAT WITH NEGATIVE “P’
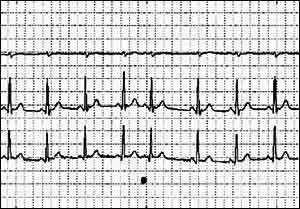
FIGURE 3- ATRIAL ECTOPIC BEATS - RUNS OF TWO



